如上章所言,特效播放主要包括应用逻辑处理和图形渲染两个阶段,其中,逻辑处理又可以看做模型对象的定义与流转
模型分层
PAG框架模型大致可以分为三部分:
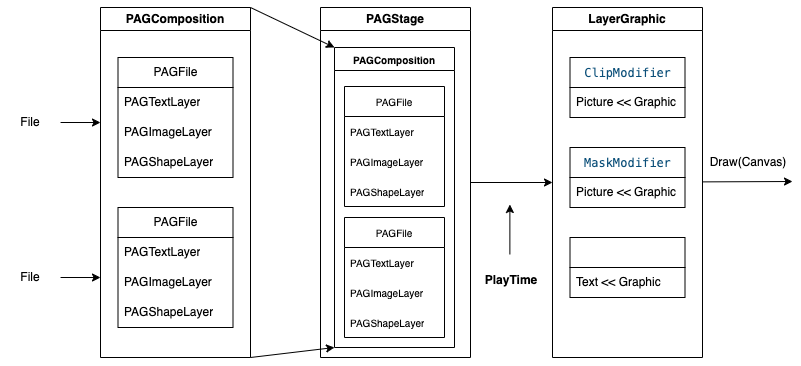
1、组件(PAGCompositon)
PAG框架支持多文件多图层渲染,PAGCompositon组件可以同时容纳多个PAGFile文件,每个PAGFile文件又可以包含多个Layer组件
PAGFile解析自File源文件,其中Layer组件可以支持元素替换,比如可以替换PAGImageLayer中PAGImage资源对象,从而实现自定义融合元素
2、图层(PAGStage)
PAGStage承载了完整的组件图层,记录了每个组件及其资源对象的映射关系,比如PAGImage及其关联的PAGImageLayer对象,实现通过资源对象查找对应Layer对象的能力
此外,PAGStage通过SequenceCache还缓存了资源对象与Graphic视图对象的映射关系,类似于渲染缓存的职责
3、图形(LayerGraphic)
组件模块加上时间戳,就生成对应时刻的图形对象Graphic,比如纹理图形Picture,或者文本图形Text
LayerGraphic作为图形模型的容器,继承自ComposeGraphic对象,包含当前播放时刻所有的图像对象,每一个图形对象可以通过装饰器添加裁切或者蒙版等多种处理效果
源码浅析
1、File文件解析
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
// 文件二进制解析 std::shared_ptr<File> File::Load(const void* bytes, size_t length, const std::string& filePath, const std::string&) { file = Codec::Decode(bytes, static_cast<uint32_t>(length), filePath); ... return file; } // File对象初始化 File::File(std::vector<Composition*> compositionList, std::vector<pag::ImageBytes*> imageList) : images(std::move(imageList)), compositions(std::move(compositionList)) { // 每一个File文件都有对应的mainComposition对象,组件元信息其实都存在compositon里面 mainComposition = compositions.back(); rootLayer = PreComposeLayer::Wrap(mainComposition).release(); ... } |
2、PAGFile构造
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 |
// 通过File构造PAGFile std::shared_ptr<PAGFile> PAGFile::MakeFrom(std::shared_ptr<File> file) { // 解析File构造组件模型 auto pagLayer = BuildPAGLayer(file, file->getRootLayer()); pagLayer->gotoTime(0); auto pagFile = std::static_pointer_cast<PAGFile>(pagLayer); ... return pagFile; } // 每一个组件对象其实都持有原始File对象 std::shared_ptr<PAGLayer> PAGFile::BuildPAGLayer(std::shared_ptr<File> file, Layer* layer) { PAGLayer* pagLayer; switch (layer->type()) { case LayerType::Text: { pagLayer = new PAGTextLayer(file, static_cast<TextLayer*>(layer)); } break; case LayerType::Image: { pagLayer = new PAGImageLayer(file, static_cast<ImageLayer*>(layer)); } break; case LayerType::PreCompose: { ... if (composition->type() == CompositionType::Vector) { auto& layers = static_cast<VectorComposition*>(composition)->layers; // 遍历组件列表 for (int i = static_cast<int>(layers.size()) - 1; i >= 0; i--) { auto childLayer = layers[i]; auto childPAGLayer = BuildPAGLayer(file, childLayer); ... } } } break; } } |
3、PAGStage图层填充
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 |
// PAGComposition可以容纳多个PAGFile - (PAGComposition *)makeComposition { PAGComposition* compostion = [PAGComposition Make:self.view.bounds.size]; PAGFile* file = [PAGFile Load:[[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"data-TimeStretch" ofType:@"pag"]]; // 可以替换PAGImage资源对象,底层其实是操作PAGImageLayer [file replaceImage:0 data:[PAGImage FromPath:[[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"test" ofType:@"png"]]]; [compostion addLayer:file]; file = [PAGFile Load:[[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"data_video" ofType:@"pag"]]; [compostion addLayer:file atIndex:0]; return compostion; } void PAGPlayer::setComposition(std::shared_ptr<PAGComposition> newComposition) { ... pagComposition = newComposition; if (pagComposition) { // 填充容器 stage->doAddLayer(pagComposition, 0); } } // 建立索引缓存 void PAGStage::addReference(PAGLayer* pagLayer) { addToReferenceMap(pagLayer->uniqueID(), pagLayer); addToReferenceMap(pagLayer->layer->uniqueID, pagLayer); if (pagLayer->layerType() == LayerType::PreCompose) { auto composition = static_cast<PreComposeLayer*>(pagLayer->layer)->composition; addToReferenceMap(composition->uniqueID, pagLayer); } else if (pagLayer->layerType() == LayerType::Image) { auto imageBytes = static_cast<ImageLayer*>(pagLayer->layer)->imageBytes; addToReferenceMap(imageBytes->uniqueID, pagLayer); auto pagImage = static_cast<PAGImageLayer*>(pagLayer)->getPAGImage(); if (pagImage != nullptr) { addReference(pagImage.get(), pagLayer); } } ... } // 可以通过资源ID查找渲染缓存 std::shared_ptr<Graphic> PAGStage::getSequenceGraphic(Composition* composition, Frame compositionFrame) { ... SequenceCache cache = {}; cache.graphic = RenderSequenceComposition(composition, compositionFrame); cache.compositionFrame = compositionFrame; sequenceCache[composition->uniqueID] = cache; return cache.graphic; } |
4、Graphic图形生成
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 |
// 播放进度 void PAGPlayer::setProgress(double percent) { auto pagComposition = stage->getRootComposition(); ... pagComposition->setProgressInternal(realProgress); } // 生成图形 void PAGPlayer::prepareInternal() { renderCache->beginFrame(); auto result = updateStageSize(); if (result && contentVersion != stage->getContentVersion()) { contentVersion = stage->getContentVersion(); Recorder recorder = {}; // 通过recorder记录每个可绘制组件Layer stage->draw(&recorder); // 导出所有图形对象 lastGraphic = recorder.makeGraphic(); } } // recorder类似于二叉树,记录了每个Layer组件当前时刻对应的Graphic void PAGComposition::draw(Recorder* recorder) { ... auto composition = preComposeLayer->composition; if (composition->type() == CompositionType::Bitmap || composition->type() == CompositionType::Video) { auto layerFrame = layer->startTime + contentFrame; auto compositionFrame = preComposeLayer->getCompositionFrame(layerFrame); auto graphic = stage->getSequenceGraphic(composition, compositionFrame); recorder->drawGraphic(graphic); } ... if (hasClip()) { // 裁切装饰器 recorder->saveClip(0, 0, static_cast<float>(_width), static_cast<float>(_height)); } // 堆栈模式处理每个视图及其子视图,保证每个视图及其子视图渲染环境一致性,比如matrix变化等 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { DrawChildLayer(recorder, childLayer.get()); } if (hasClip()) { recorder->restore(); } } |
总结
为了支持多文件多图层渲染,PAG框架设计了一套完整的框架模型,其复杂的对象继承关系,加深了代码阅读理解难度,在理解其设计思路后,才能知其然知其所以然
写在文后:
本文并未提及File文件解析过程,主要原因在于我们项目中特效使用MP4文件实现,因此暂未细研其技术细节,后续有机会再单开细聊
PAG官方暂未开源文件生成源码,如果只是针对传统的礼物特效场景,可以尝试使用MP4作为替换容器
^-^
PAGStage有点类似于PlayerItem角色
PAGComposition是PAGFile的父类啊,PAGComposition中存储的是PAGLayer吧,感觉框架图有问题
PAGComposition是PAGFile的父类吧,存储的只是PAGLayer,感觉框架图有问题
这里不是继承关系图,当多个文件组合时,PAGComposition是一个容器,包含多个PAGFile